Install Asset
Install via Godot
To maintain one source of truth, Godot Asset Library is just a mirror of the old asset library so you can download directly on Godot via the integrated asset library browser

Quick Information
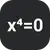
Equation solver and generator for real-valued polynomial equations up to 4th degree.Example:func example() -> void:print(ResSolver.linear(5, -10)) # Prints 2print(ResSolver.quadratic(1, 1, -6)) # Prints [-3, 2]print(ResSolver.cubic(2, -11, 12, 9)) # Prints [-0.5, 3]print(ResSolver.quartic(1, -10, 35, -50, 24)) # Prints [1, 2, 3, 4]print(ResGenerator.quartic(1, 2, 3, 4)) # Prints [1, -10, 35, -50, 24]
Real Equation Solver
Equation solver and generator for real-valued polynomial equations up to 4th degree.
Table of Content
Download
Example
func example() -> void:
print(ResSolver.linear(5, -10)) # Prints 2
print(ResSolver.quadratic(1, 1, -6)) # Prints [-3, 2]
print(ResSolver.cubic(2, -11, 12, 9)) # Prints [-0.5, 3]
print(ResSolver.quartic(1, -10, 35, -50, 24)) # Prints [1, 2, 3, 4]
print(ResGenerator.quartic(1, 2, 3, 4)) # Prints [1, -10, 35, -50, 24]
Reference
- RealEquationSolver
ResSolver
float linear(a: float, b: float) static
Returns a real root of an equation of the form: ax + b = 0
float linear_array(coeffs: Array[float]) static
See linear().
Array[float] quadratic(a: float, b: float, c: float) static
Returns a sorted array of real roots of an equation of the form: ax² + bx + c = 0.
Array[float] quadratic_array(coeffs: Array[float]) static
See quadratic().
Array[float] cubic(a: float, b: float, c: float, d: float) static
Returns a sorted array of real roots of an equation of the form: ax³ + bx² + cx + d = 0.
Warning: For large argument values, answers may be inaccurate or incorrect, e.g. >= 10_000_000.
Array[float] cubic_array(coeffs: Array[float]) static
See cubic().
Array[float] quartic(a: float, b: float, c: float, d: float, e: float) static
Returns a sorted array of real roots of an equation of the form: ax⁴ + bx³ + cx² + dx + e = 0.
Warning: For large argument values, answers may be inaccurate or incorrect, e.g. >= 10_000_000.
Array[float] quartic_array(coeffs: Array[float]) static
See quartic().
Array[float] solve(...coeffs: Array) vararg static
Returns a sorted array of the real roots of an equation based on the number of arguments.
Warning: For large argument values, answers may be inaccurate or incorrect, e.g. >= 10_000_000.
Array[float] solve_array(coeffs: Array[float]) static
See solve().
ResGenerator
Array[float] linear(r0: float) static
Returns the coefficients of a equation with the given roots, in the form: ax + b = 0. Where the leading coefficient a is always 1.
Array[float] linear_array(roots: Array[float]) static
See linear().
Array[float] quadratic(...roots: Array) vararg static
Returns the coefficients of a equation with the given roots, in the form: ax² + bx + c = 0. Where the leading coefficient a is always 1.
Array[float] quadratic_array(roots: Array[float]) static
See quadratic().
Array[float] cubic(...roots: Array) vararg static
Returns the coefficients of a equation with the given roots, in the form: ax³ + bx² + cx + d = 0, where the leading coefficient a is always 1.
Array[float] cubic_array(roots: Array[float]) static
See cubic().
Array[float] quartic(...roots: Array) vararg static
Returns the coefficients of a equation with the given roots, in the form: ax⁴ + bx³ + cx² + dx + e = 0, where the leading coefficient a is always 1.
Array[float] quartic_array(roots: Array[float]) static
See quartic().
Contributing
- Contributions are welcome. Open an issue or PR.
Equation solver and generator for real-valued polynomial equations up to 4th degree.
Example:
func example() -> void:
print(ResSolver.linear(5, -10)) # Prints 2
print(ResSolver.quadratic(1, 1, -6)) # Prints [-3, 2]
print(ResSolver.cubic(2, -11, 12, 9)) # Prints [-0.5, 3]
print(ResSolver.quartic(1, -10, 35, -50, 24)) # Prints [1, 2, 3, 4]
print(ResGenerator.quartic(1, 2, 3, 4)) # Prints [1, -10, 35, -50, 24]
Reviews
Quick Information
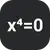
Equation solver and generator for real-valued polynomial equations up to 4th degree.Example:func example() -> void:print(ResSolver.linear(5, -10)) # Prints 2print(ResSolver.quadratic(1, 1, -6)) # Prints [-3, 2]print(ResSolver.cubic(2, -11, 12, 9)) # Prints [-0.5, 3]print(ResSolver.quartic(1, -10, 35, -50, 24)) # Prints [1, 2, 3, 4]print(ResGenerator.quartic(1, 2, 3, 4)) # Prints [1, -10, 35, -50, 24]

