Install Asset
Install via Godot
To maintain one source of truth, Godot Asset Library is just a mirror of the old asset library so you can download directly on Godot via the integrated asset library browser

Quick Information
This native Godot extension provides real and complex matrix algebra. It also includes ODE solver based on ODEINT, BoostC++ Geometry algorithms.Checkout demos:https://github.com/dmrokan/gdblas/releases/download/v1.4.0/demo.ziphttps://github.com/dmrokan/gdblas/releases/download/v1.4.0/demo3d.zip
GDBlas
This native Godot extension provides real and complex matrix algebra. It uses data structures and matrix iterators of Eigen library, also includes ODE solver based on ODEINT.
In version 1.4.0, BoostC++ Geometry algorithms are added.
Demos
- There is a demo project in
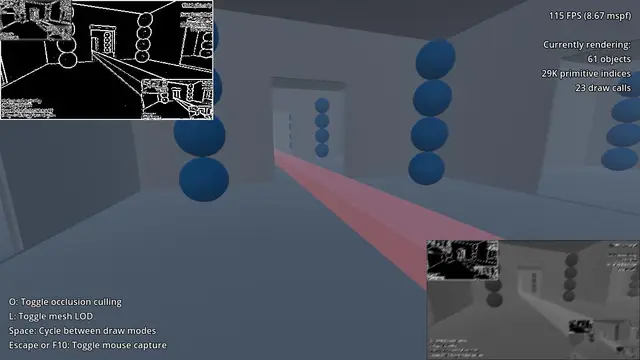
demodirectory which includes numerous tests and displacement simulation of a flexible structure. Its mathematical model can be found in my PhD thesis (Chapter 6). - 3D demo project based on a Godot example. It displays filtered versions of the texture in
Viewportas shown below.

https://gist.github.com/user-attachments/assets/aa9c1056-6da8-4c55-9c86-5937d3cd315c
An example:
var gbl = GDBlas.new()
var A = gbl.new_mat(3, 2)
var b = gbl.new_mat(2, 1)
A.from_array([ [1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6] ])
b.from_array([ [1], [-1] ])
var c = A.prod(b)
print(c.to_array())
c.abs()
print(c.to_array())
c.log()
print(c.to_array())
c.add(3)
print(c.to_array())
will print out
>>> [ [-1], [-1], [-1] ]
>>> [ [1], [1], [1] ]
>>> [ [0], [0], [0] ]
>>> [ [3], [3], [3] ]
Classes
GDBlas
Reference counted base class which is used to create new matrices
Methods
new_mat(p_rows, p_cols = -1): Creates new real matrix, Usage:
var gbl = GDBlas.new()
var A = gbl.new_mat(3, 12) # Creates a 3 by 12 real matrix
var B = gbl.new_mat(3) # Creates a 3 by 3 real matrix
var C = gbl.new_mat(Vector2i(4, 2)) # Creates a 4 by 2 real matrix
new_complex_mat(p_rows, p_cols = -1): Creates new complex matrixlinspace(p_start, p_end, p_count): Creates a column vector of linearly spaced values
var gbl = GDBlas.new()
var A = gbl.linspace(0, 1, 3) # Creates a 3 by 1 matrix with entries [ [0], [0.5], [1] ]
mat_to_image_data(p_mat_array: Array, p_channel_width: int = 1): Places the entries ofGDBlasMatobjects inp_mat_arrayinto aPackedByteArraywhich matches the data structure returned fromImage::get_data().
var gbl = GDBlas.new()
var dim = Vector2i(480, 640)
var R = gbl.new_mat(dim)
var G = gbl.new_mat(dim)
var B = gbl.new_mat(dim)
# fill and process R, G, B matrices
var pack: PackedByteArray = gbl.mat_to_image_data([ R, G, B ])
# An RGB8 formatted Image object can be created by using the data in 'pack'
area(p_polygon: PackedVector2Array): Calculates the area of polygon. Points must be ordered in clockwise (CW) direction.
Boost Geometry
Data structures
List of Boost Geometry data structures and their representations in GDScript to be used by GDBlas's bindings of Boost Geometry algorithms.
model::point≡Vector2model::linestring≡PackedVector2Arraymodel::ring≡PackedVector2Arrayif the first and last values of the array are equal.model::polygon≡ArrayofPackedVector2Arraywhere the first entry represents the outer ring and the other entries represent inner rings.ring_type model::polygon::outer≡PackedVector2Arraywhere the first and last values of the array are equal.ring_type model::polygon::inners[i]≡PackedVector2Arraywhere the first and last values of the array are equal.
model::box≡Rect2
Algorithms
areabuffercentroidclearclosest_pointsconvertconvex_hullcorrectcovered_bycrossesdensifydifferencediscrete_frechet_distancediscrete_hausdorff_distancedisjointdistanceenvelopeequalsintersectionintersectsis_emptyis_simpleis_validlengthoverlapsperimeterrelationreversesimplifysym_differencetouchestransformunion_uniquewithin
Return types and errors
The algorithms above may not be used all combinations of models. In such cases and error message is emitted and function returns an invalid value. The map of return types and invalid values are given below.
boolreturn types: Returnsint.1=true,0=false, negative value on error.intreturn types: Returnsint, negative value on error.doublereturn types: Returnsfloat,NaNon error.model::polygonreturn types: ReturnsArrayofPackedVector2Array, emptyArrayon error.model::ringreturn types: ReturnsPackedVector2Array, emptyPackedVector2Arrayon error.model::linereturn types: ReturnsPackedVector2Array, emptyPackedVector2Arrayon error.model::pointreturn types: ReturnsVector2,Vector2(NaN, NaN)on error.model::boxreturn types: ReturnsRect2,Rect2(NaN, NaN, NaN, NaN)on error.
Examples
You can check the tests in demo/GDBlasTest.gd for learning how to use.
GDBlasMat
Reference counted real or complex matrix object. A real matrix returns enries as a float and complex matrix as Vector2.
Methods
resize(m: Variant, n: int = -1): Resizes matrix to m by n if both are integer.nis not required ifmisVector2i.copy(): Creates a copy of matrix.
var gbl = GDBlas.new()
var A = gbl.new_mat(3)
var B = A.copy()
dimension(): Returns the size of matrix as aVector2iobjectget(i, j, m = -1, n = -1): Get a matrix entry or a submatrix of size m by n starting ith row and jth column. Returns0on success or error value.
var gbl = GDBlas.new()
var A = gbl.new_mat(3)
var a00: float = A.get(0, 0)
var Asub: GDBlasMat = A.get(1, 0, 2, 2) # Returns 2 by 2 sub matrix
var Ac = gbl.new_complex_mat(3)
var ac00: Vector2 = A.get(0, 0)
set(val, i = -1, j = -1): Set a matrix entry or a submatrix of size m by n starting ith row and jth column. Returns0on success or error value.
var gbl = GDBlas.new()
var A = gbl.new_mat(3)
var a00: float = A.set(1, 0, 0)
var Asub = gbl.new_mat(2)
A.set(Asub, 1, 0)
add(val): Adds a number or a matrix of same dimension. Returns0on success or error value.
var gbl = GDBlas.new()
var A = gbl.new_mat(3)
A.add(1)
var B = A.copy()
B.add(A)
mul(val): Multiplies by a number or a matrix of same dimension. Returns0on success or error value.div(val): Divides by a number or a matrix of same dimension. Returns0on success or error value. NOTE: Can not add complex matrices to a real matrixsub(val): Subtracts a number or a matrix of same dimension. Returns0on success or error value.transpose(): Transposes the matrix. Returns0on success or error value.hermitian(): Hermitian transpose of matrix. Returns0on success or error value.is_eq(other, p_eps, p_norm_type): Checks if matrices are equal, meaning that norm of their differences are less thanp_eps. Returnstrueorfalse
var gbl = GDBlas.new()
var A = gbl.new_mat(3)
var B = A.copy()
if A.is_eq(B):
print("They are equal")
fill(val): Sets all matrix entries toval.valcan be a number orVector2if it is a complex matrix. Returns0on success.eye(val): Sets all diagonal matrix entries toval.valcan be a number orVector2if it is a complex matrix. Returns0on success.reset(): Sets all entries to0.conj(): Conjugates all matrix entries. Returns0on success.real(matrix): Returns or sets the real part of complex matrix. It is equivalent toset(matrix, 0, 0)on real case.imag(matrix): Returns or sets the imaginary part of complex matrix. It returns a matrix of zeros for real matrix case.prod(matrix): Returns product of matrices.
var gbl = GDBlas.new()
var A = gbl.new_mat(3)
var B = gbl.new_mat(3, 5)
var C = A.prod(B)
It is equivalent to C=AB, column count of A and row count of B must be equal.
inv(): Computes the inverse of matrix. It can only be applied to square matrices. It will return the inverse matrix ornullif matrix is singular.from_array(arr): Sets matrix entries according to the values on 2 dimensional arrayarr. Return0on success.
var gbl = GDBlas.new()
var A = gbl.new_mat(3, 2)
A.from_array([ [1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6] ])
to_array(): Returns a 2 dimensional array filled with matrix entries.
var gbl = GDBlas.new()
var A = gbl.new_complex_mat(2, 2)
A.eye(Vector2(1, -1))
print(A.to_array())
will print
>>> [ [(1,-1), (0,0)], [(0,0), (1,-1)] ]
integrate(axis = -1): Calculates sum of matrix entries on given axis.axis=0: sums over rows,axis=1: sums of cols,axis=-1: (default) sum of all entries. Returns aGDBlasMatobject containing the sum of values.mean(axis = -1): Calculates mean of matrix entries on given axis.axis=0: mean over rows,axis=1: mean of cols,axis=-1: (default) mean of all entries. Returns aGDBlasMatobject containing the means.min(axis = -1): Finds the minimum of matrix entries on given axis.axis=0: min over rows,axis=1: min of cols,axis=-1: (default) min of all entries. Returns aGDBlasMatobject containing the minimums.max(axis = -1): Finds the maximum of matrix entries on given axis.axis=0: max over rows,axis=1: max of cols,axis=-1: (default) max of all entries. Returns aGDBlasMatobject containing the maximums.argmin(axis = -1): Finds the index of minimum of matrix entries on given axis.axis=0: min over rows,axis=1: min of cols,axis=-1: (default) min of all entries. Returns anArrayofVector2icontaining the indices of minimums.argmax(axis = -1): Finds the index of maximum of matrix entries on given axis.axis=0: max over rows,axis=1: max of cols,axis=-1: (default) max of all entries. Returns anArrayofVector2icontaining the indices of minimums.norm(norm_type): Computes $L1$, $L_{\infty}$ or Frobenius norm of matrix. Accepted arguments areGDBlas.NORM_1,GDBlas.NORM_INForGDBlas.NORM_FRO. Returnsfloat.eval_ode(p_f: Callable, p_dt: float, p_max_step: float = 1e-2): Evaluates the ordinary differential equation (ODE) defined inp_ffor an amount of time given byp_dtstarting from the current value of matrix. It can be called on only real n by 1 matrices (equivalent to a column vector). Returns the step count (how many times the ODE function is evaluated) or a negative value on error.
var A: GDBlasMat = null
func ode_fx(x: GDBlasMat, t: float):
return A.prod(x)
func some_func():
var gbl = GDBlas.new()
A = gbl.new_mat(2)
A.eye(-1)
var x = gbl.new_mat(2, 1)
x.fill(1)
x.eval_ode(ode_fx, 0.5, 1e-3) # Writes final value at t = 0.5 into x itself
conv(p_other: GDBlasMat, p_same: bool = false): Computes convolution of matrices. Ifp_sameistrue, returns the central part of the result.
var gbl = GDBlas.new()
A = gbl.new_mat(m1, n1)
A.from_array( ... ) # Fill with values.
B = gbl.new_mat(m2, n2)
B.from_array( ... ) # Fill with values.
var C = A.conv(B)
assert(C.dimension() == Vector2i(m1 + m2 - 1, n1 + n2 -1))
var D = B.conv(A, 'same')
assert(D.dimension() == Vector2i(m2, n2))
pack(p_component: int = GDBlas.BOTH_COMPONENTS): Packs matrix entries into aPackedFloat64Arrayin row major format. Argumentp_componentcan take valuesGDBlas.REAL_COMPONENT,GDBlas.IMAG_COMPONENTorGDBlas.BOTH_COMPONENTS. If both components of a complex matrix is packed imaginary part of each entry is placed right after the real component in thePackedFloat64Array. ReturnsPackedFloat64Array.unpack(p_packed_data: PackedFloat64Array, p_component: int = GDBlas.BOTH_COMPONENTS, p_step: int = 1, p_offset: int = 0): Unpacks the data inp_packed_datainto the matrix. Ifp_step = n, each nth entry in thep_packed_dataplaced into the matrix starting from the entry indexed byp_offset. Number of elements in the array divided byp_stepmust match the matrix dimension.downsample(p_factor_m: int, p_factor_n: int, p_filter: GDBlasMat = null): Returns a new matrix constructed by picking rows and columns whose index satisfyrow_index % p_factor_m == 0andcol_index % p_factor_n == 0. Ifp_filterprovided, the matrix is filtered (by convolving) by the the coefficients ofp_filterbefore down sampling.
Elementwise functions
A list of implemented math functions are given below. They operate elementwise on the matrix and modifies matrix itself instead of creating a copy. You can visit C++ stdlib documentation for mathematical meaning of these functions.
f(p_func: Callable, p_args: Array = null, p_indexed: bool = false): Appliesp_funcon each matrix entry and writes the result in place. Ifp_indexedistrue,p_funccan have additional argumens which gives the row and column number of the matrix entry.
func add_1(a):
return a + 1
func add_const(a, args: Array):
return a + args[0]
func add_const_2(a, args: Array, i: int, j: int):
if i < 1 and j < 1:
return a + args[0]
else:
return a
func some_func():
var gbl = GDBlas.new()
var A = gbl.new_mat(2, 2)
A.f(add_1)
A.f(add_const, [ 3 ])
A.f(add_const_2, [ 3 ], true)
NOTE: If the matrix is complex, first argument of callable is a Vector2 and its return type must also be Vector2.
sin()
var gbl = GDBlas.new()
var vec = gbl.linspace(-0.5, 0.5, 256)
vec.mul(2 * PI)
vec.sin() # Calculate sine of vec and write in place.
cos()abs()exp()log()log10()log2()sqrt()cbrt()tan()asin()acos()atan()sinh()cosh()tanh()atanh()erf()erfc()tgamma()lgamma()ceil()floor()trunc()round()
Build from source
git clone https://github.com/dmrokan/gdblas.git
cd gdblas
git submodule update --init --recursive
Build boost
cd boost
./bootstrap.sh
./b2 headers
You can visit Boost wiki for more information.
Build extension
scons platform=<platform> target_path=<target_path> target_name=libgdblas
You can visit Godot's build system documentation for more information.
This native Godot extension provides real and complex matrix algebra. It also includes ODE solver based on ODEINT, BoostC++ Geometry algorithms.
Checkout demos:
https://github.com/dmrokan/gdblas/releases/download/v1.4.0/demo.zip
https://github.com/dmrokan/gdblas/releases/download/v1.4.0/demo3d.zip
Reviews
Quick Information
This native Godot extension provides real and complex matrix algebra. It also includes ODE solver based on ODEINT, BoostC++ Geometry algorithms.Checkout demos:https://github.com/dmrokan/gdblas/releases/download/v1.4.0/demo.ziphttps://github.com/dmrokan/gdblas/releases/download/v1.4.0/demo3d.zip