Install Asset
Install via Godot
To maintain one source of truth, Godot Asset Library is just a mirror of the old asset library so you can download directly on Godot via the integrated asset library browser



Quick Information
A node type that smoothes scene nodes' properties by interpolating _physics_process steps.IMPORTANT NOTE:Since Godot 4.3 Beta 1 you can find built-in physics interpolation for 2D in `Project settings > Physics > Common > Physics Interpolation`.Physics interpolation for 3D is being worked on and should make it into a future release.See https://godotengine.org/article/dev-snapshot-godot-4-3-beta-1/#2d-physics-interpolation .If you can use a Godot version with built-in physics interpolation, I highly recommend using that. If you rely on an older Godot 4 version without built-in physics interpolation, please read on.-----Godot typically has 60 physics ticks per second but monitors may have different refresh rates. As a result a game may look jittery on some hardware. The Smoother node interpolates between physics process steps to ensure smooth physics animations.By default the position property is smoothed but the settings allow interpolating any properties, even custom ones, that are of a supported data type, i.e. int, float, Vector2, Vector3, Vector4, Color, Quaternion, Basis.For usage and detailed documentation please visit the GitHub repository.The latest changes addresses an issue in case the game FPS drops below the physics ticks per second.
godot-smoother-node
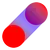
A Godot 4 node type that smoothes scene node movements by interpolating _physics_process steps.

Above: Not smoothed vs. smoothed.
Smoother node
This node interpolates properties of other nodes between their _physics_processes. The interpolation is applied in the _process loop which ensures that nodes move smoothly, even if the _physics_process is called less often than the games fps rate which is typically synced to the current screen's refresh rate.
By default only the node position is interpolated.
Visit godot-smoother-node-test-scene to download a Godot 4 sample project.
YouTube Tutorial
Usage
Basic Usage
Add the smoother.gd script to your project. Since it has a class_name it is automatically added to the available nodes of the project.
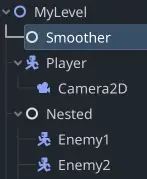
Simply add the Smoother node as a child to your root node (like a level root). By default it will interpolate the position of all supported[^1] and relevant[^2] nodes in the scene.
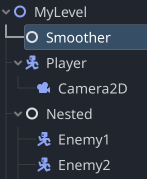
[^1]: Currently RigidBody2D and RigidBody3D are not supported.
[^2]: Nodes that have no custom _physics_process are automatically ignored. So are target properties that a node may not have.
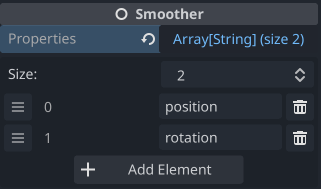
Properties
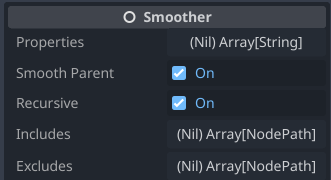
Smoother default options are:
- properties:
Array[String]=["position"][^3] — The listed properties are interpolated[^4] unless a node does not have the property in which case it will be ignored for that particular node. - smooth_parent:
bool=true— Include the parent node for interpolation. - recursive:
bool=true— Include recursive children. Note that recursive is relative to the Smoother's parent. In a way the Smoother node attaches to a parent and takes the parent as the base for its operations.[^5] - includes:
Array[NodePath]=[]— Any node listed in this array will be smoothed unless listed inexcludes. - excludes:
Array[NodePath]=[]— Any node listed in this array will be excluded from smoothing. This overwrites any options above.
[^3]: Note that at the moment of writing, Godot does not display the default ["position"] value for properties in the inspector, even though the value applies. This may be fixed in a future Godot release.
[^4]: Interpolation only works properties of data types that are supported by lerp, i.e. int, float, Vector2, Vector3, Vector4, Color, Quaternion, Basis
[^5]: The Smoother node cannot access nodes above its parent node, it can only act on its parent, parent's children or parent's nested children, except a node higher in the tree hierarchy is an item in includes.
Adding other properties that the Smoother will attempt to interpolate is as easy as adding the property name strings.
Performance Optimisations
For large levels you may want to optimise things (as you probably should regardless of using the Smoother node). A good approach would be to use the VisibleOnScreenNotifier2D/VisibleOnScreenNotifier3D and use their screen_entered and screen_exited signals to update the includes or excludes array.
Method 1: excludes
Add all off-screen moveable nodes to excludes and remove them when they come on-screen, e.g.
func _on_node_screen_entered(node:Node) -> void:
$Smoother.add_exclude_node(node)
func _on_node_screen_exited(node:Node) -> void:
$Smoother.add_exclude_node(node)
Since excludes overwrite all other Smoother settings this is the most flexible option.
One caveat is that on entering the tree, the VisibleOnScreenNotifier2D/VisibleOnScreenNotifier3D do not fire the screen_exited signal, so you may have to emit this in a Node's _enter_tree, e.g.
func _enter_tree() -> void:
if !$VisibleOnScreenNotifier2D.is_on_screen():
_on_screen_exited()
Method 2: includes
Add all on-screen moveable nodes to includes and remove them when they come off-screen, e.g.
func _on_node_screen_entered(node:Node) -> void:
$Smoother.add_include_node(node)
func _on_node_screen_exited(node:Node) -> void:
$Smoother.remove_include_node(node)
Since includes adds nodes but does not interfere with other options you probably should set the smooth_parent and recursive options to false.
On entering the tree, the VisibleOnScreenNotifier2D/VisibleOnScreenNotifier3D automatically fire the screen_entered signal, so nothing needs to be done.
For Both Methods
Either way it's probably a good idea to emit the screen_exited signal on _exit_tree to cleanup the inludes or excludes array, e.g.
func _exit_tree() -> void:
emit_signal("screen_exited", self)
The godot-smoother-node-test-scene uses performance optimisations in level2d.gd and some sprite nodes that emit signals as mentioned above.
Debugging
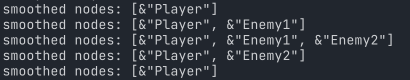
You can always check the currently smoothed nodes to see if your performance optimisation works as intended, e.g.
print("smoothed nodes: ", $Smoother.smoothed_nodes.map(func (node:Node): return node.name))
The above code displays the currently smoothed nodes in the Godot debugger when the includes or excludes array is updated:
Teleporting
When teleporting a node (changing the position) you may want to call reset_node(node) or reset_node_path(path), otherwise a teleport may not work as expected, e.g.
func _on_node_teleport_started(node: Node) -> void:
$Smoother.reset_node(node)
Notes
Collision Detection
Collision detection still happens in the _physics_process, so if the physics_ticks_per_second value in the project settings is too low you may experience seemingly incorrect or punishing collision detection. The default 60 physics_ticks_per_second should a good choice. To test this node you may want to temporarily reduce physics ticks to a lower value and toggle this node's process mode on and off. The godot-smoother-node-test-scene sample project has only 13 physics_ticks_per_second for demonstration purposes (not recommended for a "real" project). As a result collision detection is quite inaccurate.
Always the First Child
The code will automatically keep the Smoother node as the first child of its parent node because its _physics_process and _process code must run before nodes that are interpolated by it.
Process Priority
When smooth_parent is enabled the process_priority will be kept at a lower value than the parent's, i.e. it will be processed earlier, again because the Smoother's _physics_process and _process code must run before nodes that are interpolated by it.
Data Structure
The core of this class is the _properties dictionary which holds _physics_process origin and target values of the relevant nodes and properties. These values are then interpolated in _process.
For easier understanding of the code, the structure is:
_properties[node][property][0] # origin value of a node's property
_properties[node][property][1] # target value of a node's property
So for example:
_properties
├── Player
│ └── position
│ ├── 0:Vector2 = {x: 0, y: 0} # origin
│ └── 1:Vector2 = {x: 10, y: 20} # target
│ └── rotation
│ ├── 0:float = 0 # origin
│ └── 1:float = 15 # target
├── Enemy
│ └── position
│ ├── 0:Vector2 = {x: 100, y: 0} # origin
│ └── 1:Vector2 = {x: 70, y: 0} # target
│ └── rotation
│ ├── 0:float = 0 # origin
│ └── 1:float = -5 # target
:
etc.
Limitations
RigidBody2D / RigidBody3D
Currently this class does not work with RigidBody2D or RigidBody3D nodes. Please check out https://github.com/lawnjelly/smoothing-addon/ which has a more complicated setup but rewards the effort with more precision and less limitations. Or help to make this code work with rigid bodies if it's possible at all.
One Step Behind
Interpolation is one _physics_process step behind because we need to know the origin and target values for an interpolation to occur, so in a typical scenario this means a delay of 1/60 second which is the default physics_ticks_per_second in the project settings.
No Look Ahead
Interpolation does not look ahead for collision detection. That means that for example if a sprite falls to hit the ground and the last _physics_process step before impact is very close to the ground, interpolation will still occur on all _physics frames between which may have a slight impact cushioning effect. However, with 60 physics fps this is hopefully negligible.
Godot 4
This class is written in GDScript 2 for Godot 4+, but feel free to get in touch and we can add a godot-3 branch or fork the project and make adjustments. It's probably not too hard to backport since it only relies on other nodes' properties, the position property by default.
Support
I'm fairly new to Godot, so if you find any bugs or have suggestions for performance improvements in the Smoother code for example, please let me know.
I haven't tested this much yet, primarily only in the 2d and 3d test levels in the godot-smoother-node-test-scene.
A node type that smoothes scene nodes' properties by interpolating _physics_process steps.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
Since Godot 4.3 Beta 1 you can find built-in physics interpolation for 2D in `Project settings > Physics > Common > Physics Interpolation`.
Physics interpolation for 3D is being worked on and should make it into a future release.
See https://godotengine.org/article/dev-snapshot-godot-4-3-beta-1/#2d-physics-interpolation .
If you can use a Godot version with built-in physics interpolation, I highly recommend using that. If you rely on an older Godot 4 version without built-in physics interpolation, please read on.
-----
Godot typically has 60 physics ticks per second but monitors may have different refresh rates. As a result a game may look jittery on some hardware. The Smoother node interpolates between physics process steps to ensure smooth physics animations.
By default the position property is smoothed but the settings allow interpolating any properties, even custom ones, that are of a supported data type, i.e. int, float, Vector2, Vector3, Vector4, Color, Quaternion, Basis.
For usage and detailed documentation please visit the GitHub repository.
The latest changes addresses an issue in case the game FPS drops below the physics ticks per second.
Reviews
Quick Information

A node type that smoothes scene nodes' properties by interpolating _physics_process steps.IMPORTANT NOTE:Since Godot 4.3 Beta 1 you can find built-in physics interpolation for 2D in `Project settings > Physics > Common > Physics Interpolation`.Physics interpolation for 3D is being worked on and should make it into a future release.See https://godotengine.org/article/dev-snapshot-godot-4-3-beta-1/#2d-physics-interpolation .If you can use a Godot version with built-in physics interpolation, I highly recommend using that. If you rely on an older Godot 4 version without built-in physics interpolation, please read on.-----Godot typically has 60 physics ticks per second but monitors may have different refresh rates. As a result a game may look jittery on some hardware. The Smoother node interpolates between physics process steps to ensure smooth physics animations.By default the position property is smoothed but the settings allow interpolating any properties, even custom ones, that are of a supported data type, i.e. int, float, Vector2, Vector3, Vector4, Color, Quaternion, Basis.For usage and detailed documentation please visit the GitHub repository.The latest changes addresses an issue in case the game FPS drops below the physics ticks per second.

